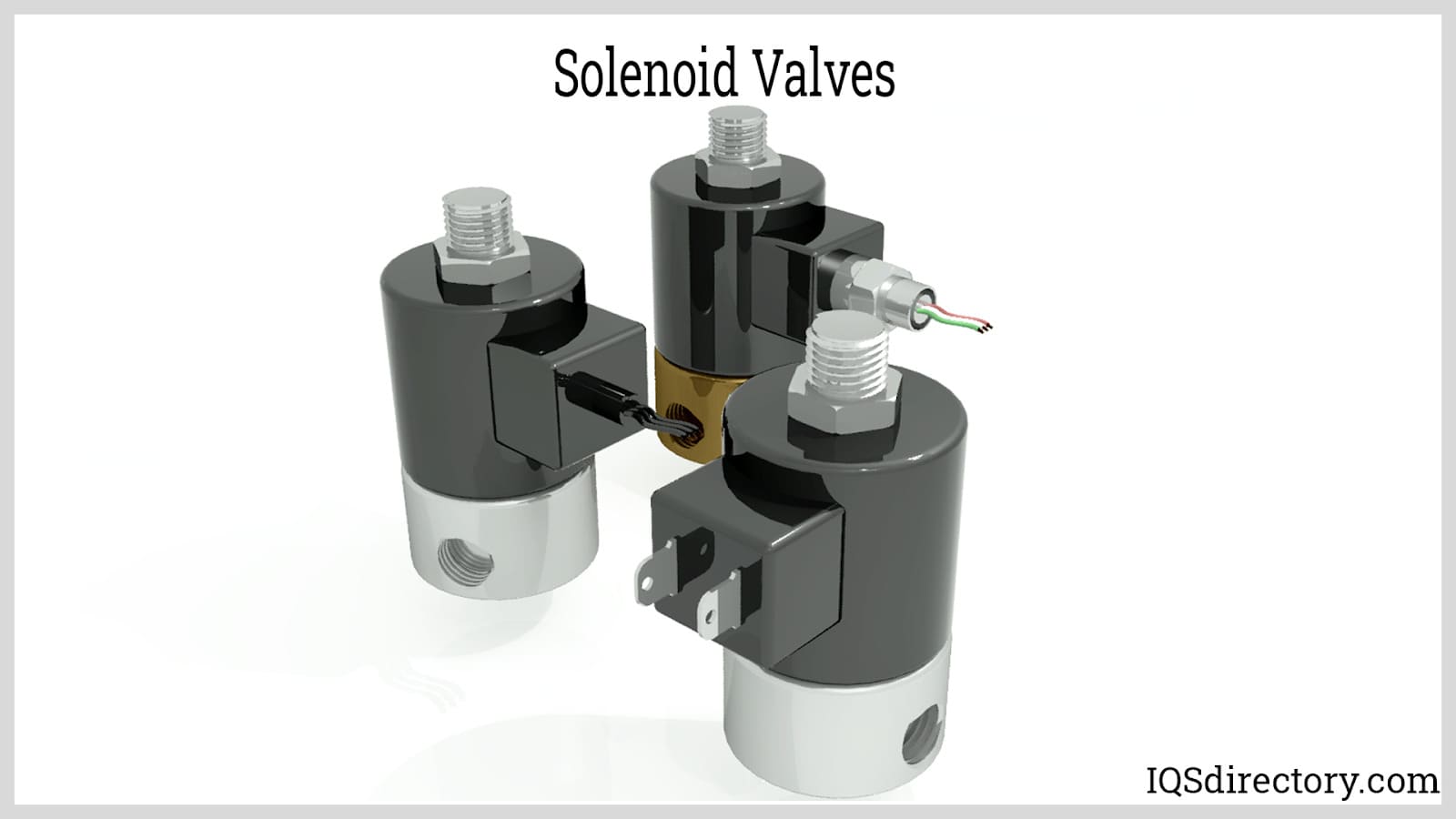
An electromechanical valve for controlling the flow of liquid or gas is called a solenoid valve. The most popular solenoid valves are direct-acting (direct-driven) and pilot-driven (or pilot-controlled). Pilot-controlled valves open and close the central orifice in the valve body. The most common variety of solenoid valves is pilot-driven valves. Despite being the only flow path in the valve, direct-driven solenoid valves open or close the primary valve orifice directly. Applications or systems that require low flow rates or low-pressure differentials across the valve orifice use direct-driven solenoid valves. Solenoid valves come in a variety of varieties. Read More…
Solenoid Solutions manufacturers custom direct-acting 2 and 3-way solenoid valves and multi-valve manifolds for OEMs in the medical, appliance, transportation, power generation and industrial equipment markets.
Our solenoid valves are all tested in house following very strict quality guidelines. We opened our doors in 1936 and ever since then we have been committed to bringing top of the line products and customer service that cannot be beat!
At Plast-O-Matic Valves, we are dedicated to designing and manufacturing high-performance fluid control solutions, with solenoid valves as a core part of our expertise. We take pride in engineering these valves with precision and reliability, ensuring they deliver consistent performance in demanding applications across a wide range of industries.

At Brandstrom Instruments, we are dedicated to delivering reliable and innovative solutions in fluid control, specializing in the design and manufacturing of high-quality solenoid valves. With decades of experience in engineering precision components, we take pride in offering products that meet the strict demands of industries requiring accurate flow regulation, durability, and efficiency.

We are proud to be DEMA® Engineering Company, a trusted name in fluid control and dispensing solutions. With decades of expertise, we design and manufacture high-quality solenoid valves that deliver reliable performance in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.

At Aquatrol, we take pride in being a trusted manufacturer of high-quality solenoid valves designed for dependable performance across a wide range of industries. With decades of hands-on expertise, we have built a reputation for precision engineering, innovative solutions, and a commitment to excellence that ensures every product we deliver meets the highest standards.

More 3 Way Solenoid Valve Manufacturers

Comprehensive Guide to 3-Way Solenoid Valves: Operation, Types, Applications, and Sourcing
How Do 3-Way Solenoid Valves Function?
3-way solenoid valves are critical components for controlling the flow of gases or liquids in piping systems. These electrically actuated valves are engineered to open, close, dose, distribute, or mix process media, making them indispensable in industrial automation, HVAC, fluid handling, and process control. The function of a solenoid valve is defined by its circuit design and application, whether it’s for isolating flow, diverting media, or enabling precise process control.
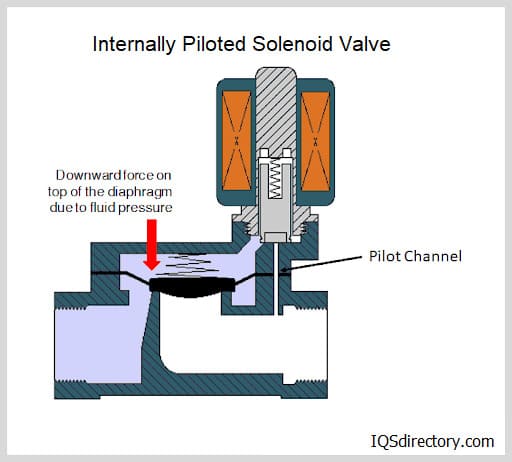
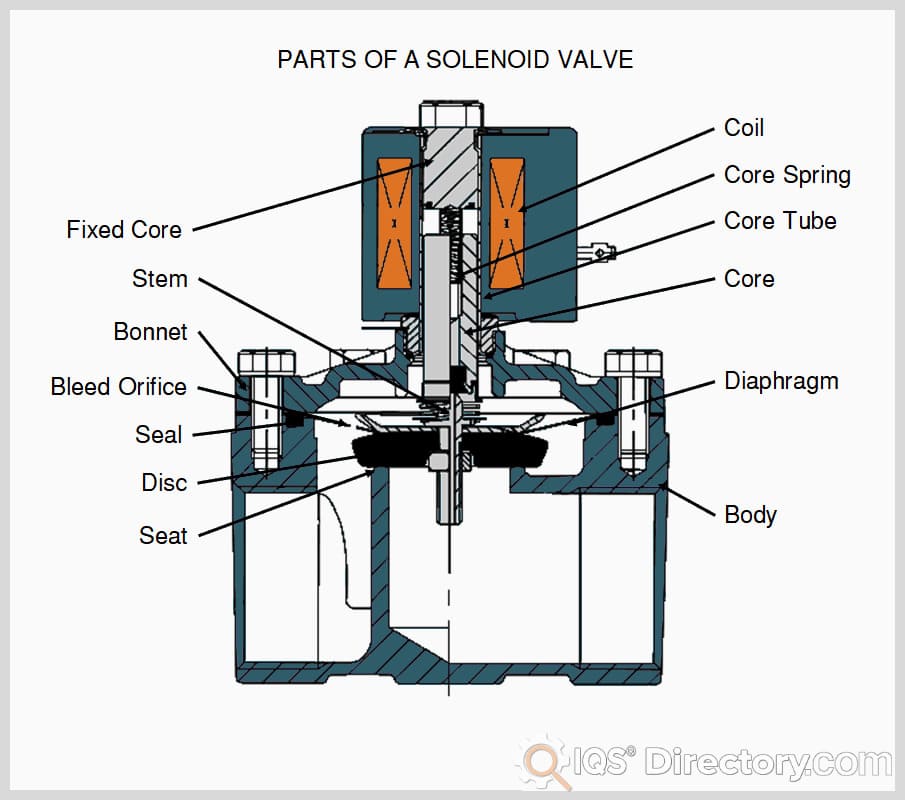
At the heart of every 3-way solenoid valve is an electromechanical solenoid, which consists of an electric coil wound around a ferromagnetic core known as a plunger. When the valve is at rest, the plunger seals an internal orifice, preventing or directing the flow as needed. Upon electrical activation, the coil generates a magnetic field that moves the plunger, altering the flow path within the valve. This simple yet robust principle is the foundation for solenoid valve operation across industries.
The valve body and solenoid work in tandem: the coil, often constructed from tightly wound copper wire, encases the plunger, which is precisely machined from iron or steel. The housing not only protects internal components but also focuses the magnetic field, maximizing the efficiency of the valve’s actuation. Whether you require a normally closed solenoid valve (NC) or a normally open solenoid valve (NO), the operational state of the valve without power determines its suitability for your application.
Detailed Working Principle of a 3-Way Solenoid Valve
When electrical current energizes the coil, electromagnetic induction pulls the plunger against a spring force. This motion opens or closes specific orifices within the valve, redirecting the flow between three ports. In a normally closed configuration, the valve blocks flow until energized; in a normally open configuration, the valve permits flow until power is applied. This characteristic enables rapid switching, remote operation, automation, and integration into safety circuits.
For AC-powered solenoid valves, a shading coil (or shading ring) is incorporated to reduce noise and vibration, ensuring smooth, quiet operation. This ring—typically copper or aluminum—creates a phase-shifted magnetic field, stabilizing the plunger and preventing mechanical chatter. The result is improved durability, reliable actuation, and reduced downtime in mission-critical systems.
Types of 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Understanding the different 3-way solenoid valve types is crucial when specifying a valve for your system. The primary configurations include:
3-Way Normally Open Solenoid Valves
Featuring three ports—the stop port, body orifice port, and cavity port—a 3-way normally open solenoid valve maintains an open flow path when de-energized. Upon coil actuation, the plunger shifts to block the body orifice and open the stop orifice, enabling alternate flow paths. This design is often utilized in systems that require fail-safe open conditions or emergency venting. Typical applications include pneumatic controls, fuel lines, and process venting where constant flow must be maintained unless interrupted by a control signal.

3-Way Normally Closed Solenoid Valves
A 3-way normally closed solenoid valve also has three ports—cavity, body orifice, and stop—but the flow path is blocked in the de-energized state. When power is applied, the plunger lifts, opening the body orifice and closing the stop orifice, allowing flow through the valve. NC solenoid valves are widely used in applications where fluid or gas flow needs to be securely blocked unless permitted, such as in water treatment, irrigation systems, medical equipment, analytical instrumentation, and automated shut-off controls.
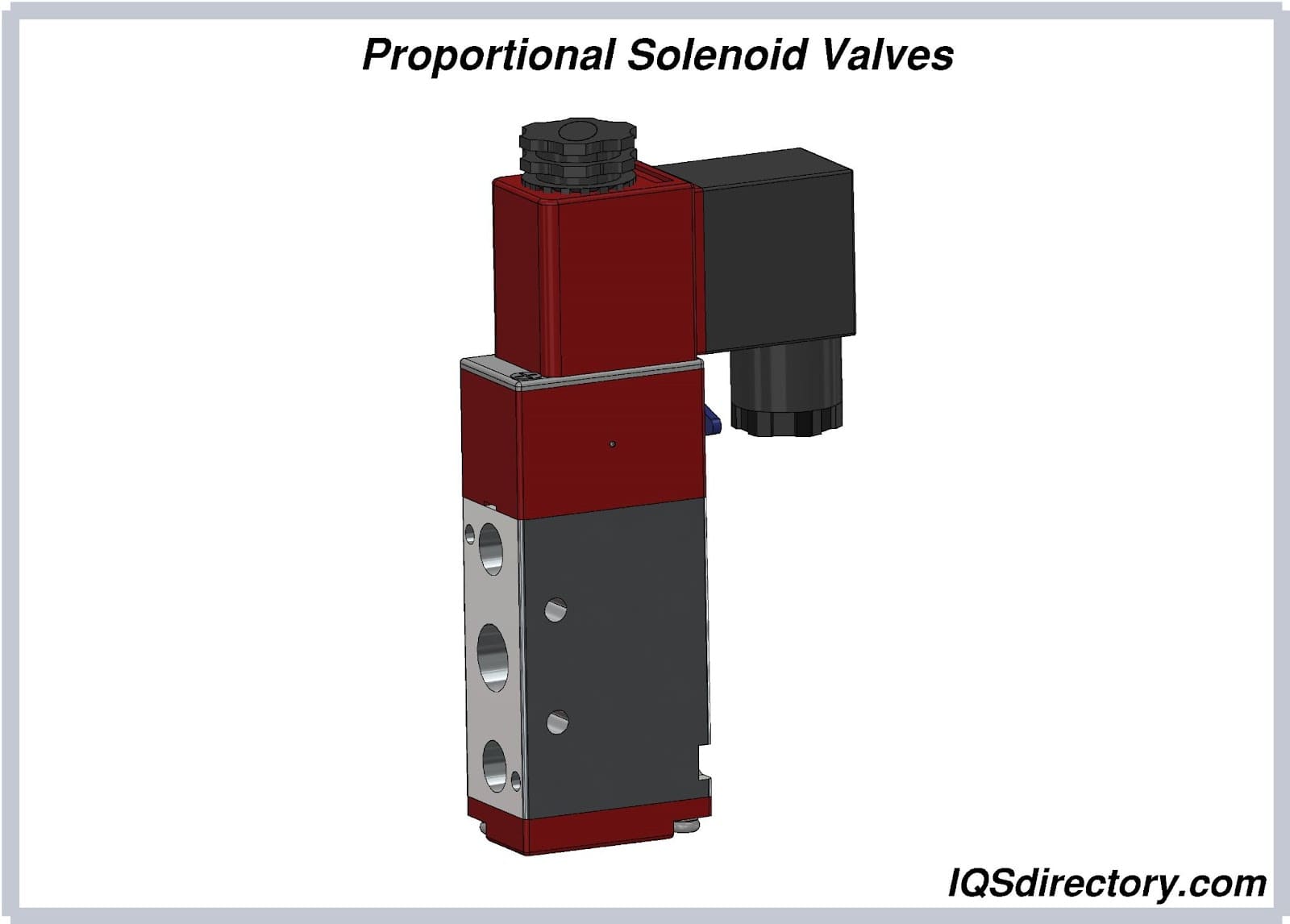
3-Way Directional Control Solenoid Valves
These valves provide precise directional control of media, making them ideal for use as pilot valves in actuators, cylinders, and complex process machinery. By alternating which orifice is open or closed, 3-way directional solenoid valves can switch flow between two outputs, vent a line, or mix/distribute different process fluids. Their versatility makes them highly valuable for automation, robotics, and motion control systems.

Key Considerations When Selecting a 3-Way Solenoid Valve Type
- Media compatibility (air, water, oil, steam, chemicals, inert gases)
- Voltage and power supply (AC, DC, low voltage, high voltage)
- Response time and actuation speed
- Operating pressure and flow rate requirements
- Temperature range and environmental conditions
- Mounting orientation and footprint
- Certifications (UL, CE, RoHS, ATEX, FDA, NSF)
- Maintenance and serviceability
The Benefits of 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Opting for a 3-way solenoid valve delivers a range of operational and economic advantages, especially when compared to manual or less flexible valve options. Here are the main benefits of choosing a 3-way solenoid valve for your system:
- Rapid response time: Enables instant switching for high-speed automation and process control.
- Low power consumption: Efficient design reduces electrical load, cutting energy costs.
- Remote operation: Easily integrated into PLCs, control panels, and IoT systems for remote actuation and monitoring.
- Versatility: Compatible with a wide range of process media, including aggressive chemicals, steam, and purified water, making them suitable for diverse industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, water treatment, and petrochemicals.
- Cost-effectiveness: Offers affordable, reliable replacements for more complex mechanical valves or manual switches.
- Flexible voltage options: Available in both DC and AC voltages and in various coil voltages to suit global standards.
- Wide temperature range: Suited for both cryogenic and high-temperature applications thanks to robust materials of construction.
- Leak prevention: Engineered to block external leaks, enhancing safety and environmental compliance.
- Flexible installation: Can be mounted in vertical or horizontal orientations, maximizing space utilization in tight control panels or process skids.
- Minimal maintenance: Simple design allows for easy inspection, cleaning, and replacement, reducing downtime and lifecycle costs.
Use Cases and Typical Applications for 3-Way Solenoid Valves
3-way solenoid valves are found in a myriad of industries due to their versatility and dependability. Below are some of the most common use cases and application scenarios:
- Industrial automation: Used to control pneumatic actuators, hydraulic cylinders, and process lines. Key for sequential machine operations, packaging, bottling, and robotics.
- HVAC systems: Manage refrigerant or chilled water flow, mix hot and cold streams, or switch between supply and return lines for efficient climate control.
- Medical and laboratory equipment: Precise dosing and mixing of fluids in analyzers, sterilizers, and dialysis machines. Enables high reliability in critical healthcare environments.
- Water treatment and filtration: Automate backwashing, media switching, and chemical injection in municipal, industrial, and commercial water systems.
- Automotive and transportation: Fuel switching, emission controls, and air suspension systems depend on fast, reliable 3-way solenoid valves.
- Food and beverage processing: Sanitary 3-way valves control ingredient blending, CIP (clean-in-place) cycles, and flow diversion in bottling or filling lines.
- Power generation and energy: Steam control, turbine bypass, and cooling water management in power plants and renewable energy systems.
- Oil & gas: Manage sampling, venting, and pilot control in upstream, midstream, and downstream operations.
- Compressed air systems: Release or direct air flow in compressor circuits, dryers, and pneumatic tools.
- Construction machinery: Enable multidirectional functions in equipment with fixed displacement pumps, switching hydraulic flow paths for various operational modes.
- Laboratory automation: Enable precise switching of reagents or samples in automated fluidic platforms.
- Fire suppression systems: Direct gas or liquid fire suppressant media, ensuring rapid response in emergency conditions.
Real-World Example Applications
- Vent valve control in steam exhaust systems—directing steam to condenser coils or atmosphere using solenoid actuation.
- Pneumatic circuit switching in robotics, allowing for rapid changes in actuator direction or function using a series of 3-way valves.
- Switching flow paths in analytical instruments for automated sample preparation or media selection.
- Combining or diverting chemical streams in process skids, maximizing flexibility in modular manufacturing plants.
Frequently Asked Questions About 3-Way Solenoid Valves
What is the difference between a 2-way and a 3-way solenoid valve?
A 2-way solenoid valve controls flow between two ports (open or closed), while a 3-way solenoid valve has three ports, enabling diverting, mixing, or alternate flow paths. For more information, see our 2-way solenoid valve guide.
How do I choose the correct 3-way solenoid valve for my process?
Consider your application’s media type, pressure, temperature, required flow rate, voltage compatibility, and installation constraints. Review the certifications needed for your industry (such as food-grade or explosion-proof ratings). Explore leading manufacturers, compare technical datasheets, and consult with a solenoid valve specialist to ensure a perfect fit.
Are 3-way solenoid valves suitable for aggressive or corrosive fluids?
Yes, many 3-way solenoid valves are available in materials like stainless steel, brass, or engineered polymers to ensure chemical compatibility. Verify wetted materials and seal types for resistance to your specific process media.
What maintenance do 3-way solenoid valves require?
Routine inspection for debris, periodic cleaning of the orifice and plunger, and coil electrical checks. For demanding environments, select valves with replaceable seats and seals to extend service life.
Can 3-way solenoid valves be used for both liquid and gas applications?
Absolutely. These valves are engineered for air, water, oil, inert gases, steam, and more. Always consult manufacturer recommendations for maximum allowable pressures and flow rates for each media.
How to Source the Right 3-Way Solenoid Valve Supplier
Choosing the best supplier for 3-way solenoid valves is a crucial step in ensuring system reliability, regulatory compliance, and long-term performance. Here’s a step-by-step approach to help buyers, engineers, and procurement specialists make informed decisions:
- Define your specifications: List all process requirements—media, pressure, temperature, flow rate, response time, certifications, and electrical standards.
- Research reputable manufacturers and distributors: Look for industry leaders with proven expertise, strong technical support, and a track record of high-quality products. Some top brands include ASCO, Parker, Burkert, SMC, and Danfoss.
- Compare suppliers: Evaluate at least 4 to 5 companies using our curated list of 3-way solenoid valve suppliers. Review each business’s profile for areas of experience, certifications, and capabilities.
- Request technical documentation and samples: Examine datasheets, CAD drawings, installation guides, and product certifications. Ask for sample valves if needed to validate performance.
- Evaluate pricing and lead time: Balance cost, delivery schedules, and after-sales support. Consider warranty, return policies, and availability of replacement parts.
- Engage with the supplier: Use our contact forms or RFQ tools to request quotes, technical consultations, and custom solutions for your project.
Our proprietary website previewer enables you to explore supplier offerings efficiently. Once you’ve reviewed your options, use our unified RFQ form to reach out to multiple suppliers and streamline your procurement process.
Key Decision Factors When Buying 3-Way Solenoid Valves
- Valve material (brass, stainless steel, plastic, special alloys)
- Seal and seat materials (NBR, EPDM, FKM, PTFE, etc.)
- Port size, thread type, and connection style
- Enclosure rating (IP65, IP67, explosion-proof, washdown)
- Response time and duty cycle
- Manufacturer reputation and customer support
- Availability of technical support and spare parts
Ready to Select or Specify a 3-Way Solenoid Valve?
Not sure which 3-way solenoid valve best fits your application? Ask yourself:
- What media will flow through the valve—air, water, oil, aggressive chemicals, or steam?
- What are the maximum and minimum pressure and temperature ranges for your system?
- Is fast response or fail-safe operation critical for your process?
- Do you need manual override, visual position indicators, or special certifications?
- Will the valve be installed indoors, outdoors, or in hazardous/explosive environments?
If you’re unsure, contact our solenoid valve experts for personalized support, product recommendations, and application engineering.
Explore More Solenoid Valve Insights & Resources
- Learn about 2-way, 4-way, and specialty solenoid valves
- Review key differences between direct acting and pilot operated solenoid valves
- Discover industry-specific solutions for food processing, pharmaceuticals, HVAC, water treatment, and automation
- Get answers to more solenoid valve FAQs
- Request a quote for your next project or bulk order
Whether you’re designing a new system, retrofitting an existing one, or troubleshooting challenging process conditions, 3-way solenoid valves offer the flexibility, reliability, and performance required in today’s demanding industrial environments. Leverage our resources to make informed decisions and optimize your fluid control solutions.









 Ball Valves
Ball Valves Butterfly Valves
Butterfly Valves Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps Check Valves
Check Valves Diaphragm Valves
Diaphragm Valves Flow Meters
Flow Meters Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pumps Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic Valves Metering Pumps
Metering Pumps Solenoid Valves
Solenoid Valves Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum Pumps Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services