A proportional control valve alters the size of the flow path using a restrictor to control the fluid flow rate. The regulated flow rate then modifies system variables that impact a process: level, pressure, and temperature. Weight, thickness, humidity, density, pH, color, and viscosity are minor factors in this alteration. Read More…
Solenoid Solutions manufacturers custom direct-acting 2 and 3-way solenoid valves and multi-valve manifolds for OEMs in the medical, appliance, transportation, power generation and industrial equipment markets.
Our solenoid valves are all tested in house following very strict quality guidelines. We opened our doors in 1936 and ever since then we have been committed to bringing top of the line products and customer service that cannot be beat!
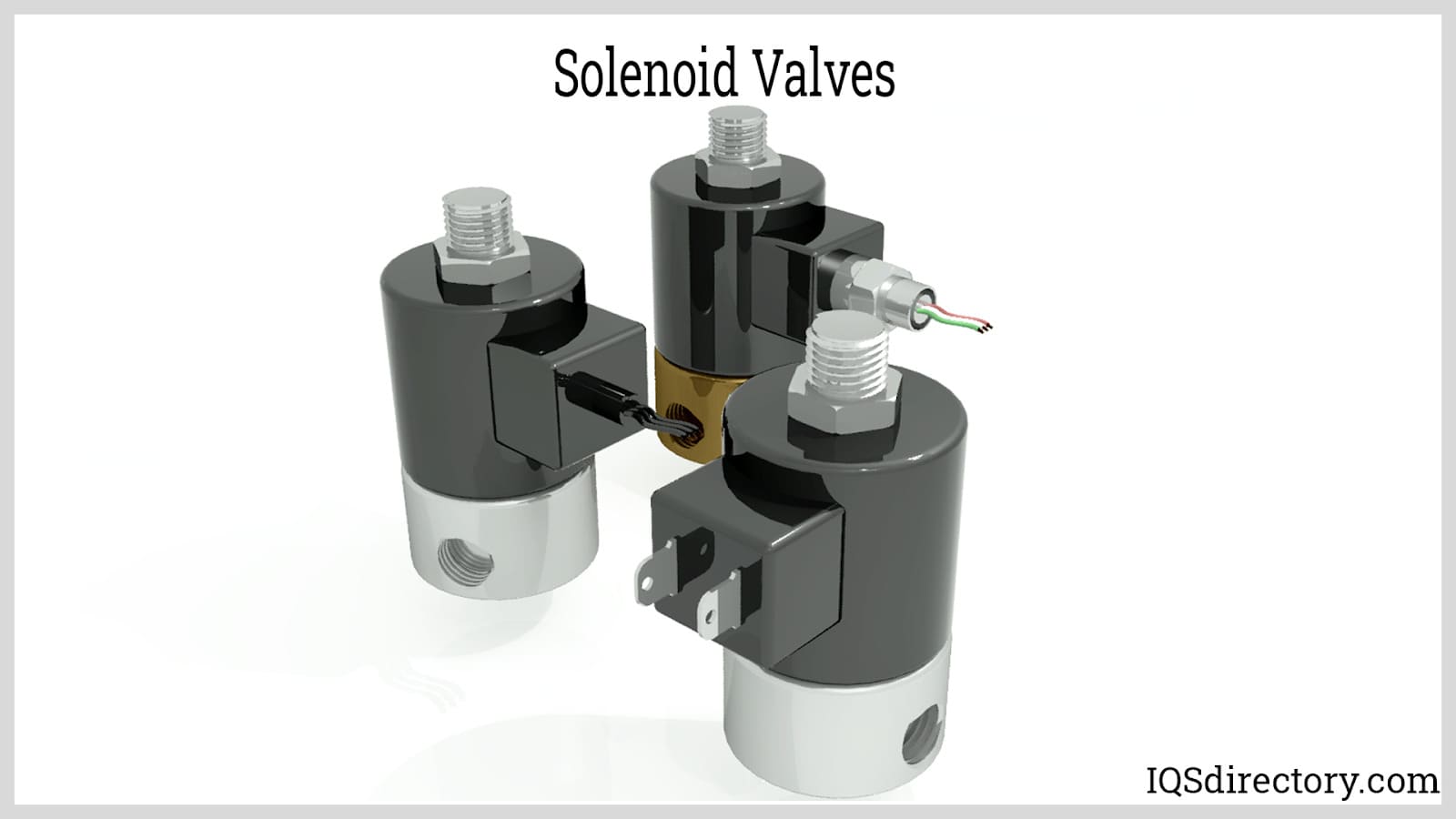
At Plast-O-Matic Valves, we are dedicated to designing and manufacturing high-performance fluid control solutions, with solenoid valves as a core part of our expertise. We take pride in engineering these valves with precision and reliability, ensuring they deliver consistent performance in demanding applications across a wide range of industries.

At Brandstrom Instruments, we are dedicated to delivering reliable and innovative solutions in fluid control, specializing in the design and manufacturing of high-quality solenoid valves. With decades of experience in engineering precision components, we take pride in offering products that meet the strict demands of industries requiring accurate flow regulation, durability, and efficiency.

We are proud to be DEMA® Engineering Company, a trusted name in fluid control and dispensing solutions. With decades of expertise, we design and manufacture high-quality solenoid valves that deliver reliable performance in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.

At Aquatrol, we take pride in being a trusted manufacturer of high-quality solenoid valves designed for dependable performance across a wide range of industries. With decades of hands-on expertise, we have built a reputation for precision engineering, innovative solutions, and a commitment to excellence that ensures every product we deliver meets the highest standards.

More Proportional Solenoid Valve Manufacturers

Proportional Solenoid Valves: Selection, Working Principle, Applications, and Buying Guide
Proportional solenoid valves are essential components in fluid control systems, offering precise and responsive modulation of flow rates, pressure, and direction in a wide range of industrial, commercial, and laboratory applications. Unlike traditional on/off solenoid valves, proportional solenoid valves enable continuous adjustment, allowing for highly accurate process control and energy efficiency. This in-depth guide covers the operating principles, selection criteria, key benefits, typical use cases, and expert tips for sourcing the right proportional solenoid valve for your specific needs.
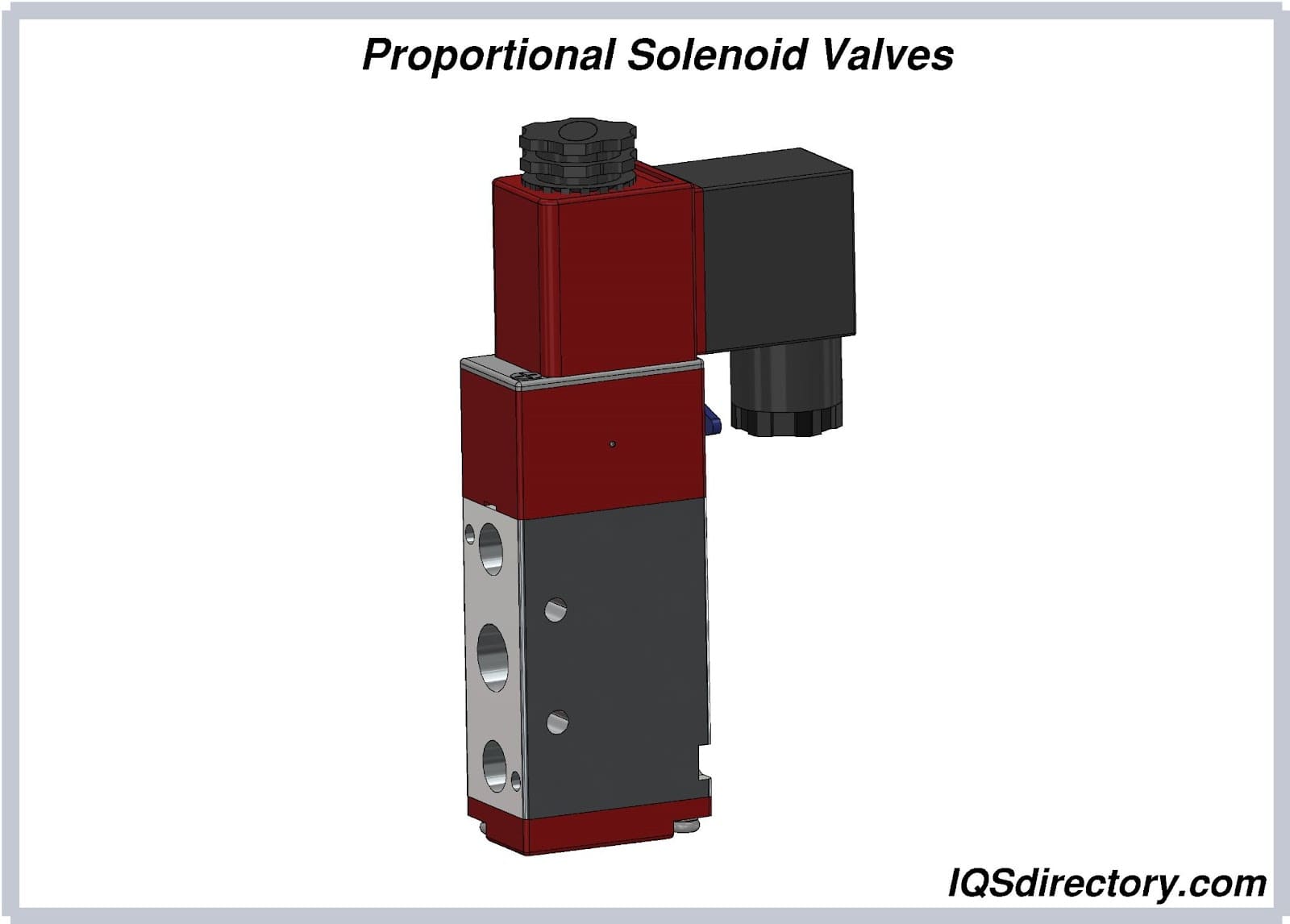
What Is a Proportional Solenoid Valve?
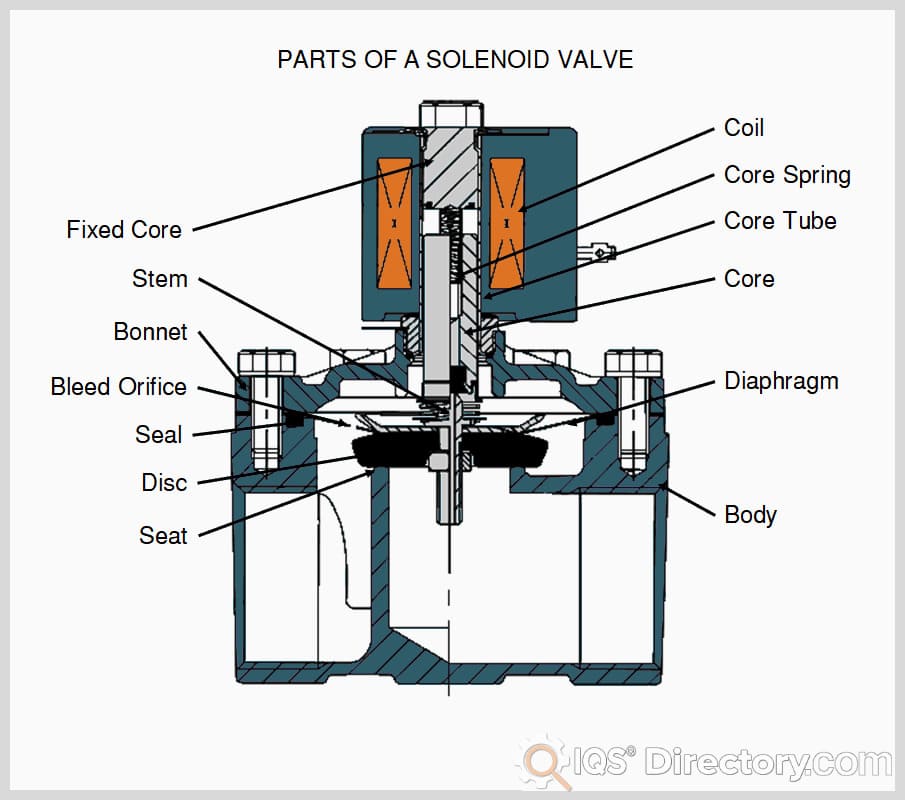
A proportional solenoid valve is an electromechanical device that controls the flow of liquids or gases by varying the position of a restrictor element (such as a plunger or spool) in response to an electrical control signal, usually from a programmable logic controller (PLC) or other automation system. The position of the restrictor is directly proportional to the input signal, enabling smooth and precise regulation of the process variable—such as flow rate, pressure, or temperature.
In many automated systems, a signal from an actuator precisely adjusts the restrictor in an automatic control valve. For example, a solenoid serves as the actuator for a proportional control solenoid valve, facilitating variable valve positioning for precise process management. While a direct-operated solenoid valve can operate at different valve settings, a standard 2-way direct-acting proportional solenoid valve typically offers two main switching states: on and off. However, proportional solenoid valves are engineered to provide variable positions between fully open and fully closed, enabling a fine-tuned response to real-time control signals.
Key Features:
- Continuous modulation of flow or pressure
- Fast response and high precision
- Compact and reliable design
- Compatibility with a wide range of media (liquids, gases, air, steam)
- Low power consumption and efficient operation
Operating Principle of Proportional Solenoid Valves
The proportional solenoid valve’s core operating principle relies on the relationship between the electrical control signal and the mechanical movement of the restrictor (plunger or spool). When a varying DC voltage or a pulse-width modulated (PWM) signal is applied to the solenoid coil, the resulting electromagnetic force moves the plunger proportionally, altering the valve opening and consequently adjusting the flow of the medium through the valve.
In theory, the plunger could be precisely controlled with a variable DC voltage. However, in practice, factors like static friction at the plunger’s guiding points can reduce sensitivity and introduce hysteresis—where the valve’s response lags behind changes to the control signal. To mitigate these effects and enhance sensitivity, PWM is widely used. PWM rapidly switches the solenoid on and off, with the duty cycle (the ratio of on-time to the entire cycle) determining the average power delivered to the solenoid.
This method causes the plunger to oscillate rapidly with a small amplitude, maintaining consistent sliding friction and positioning the plunger in a dynamic equilibrium. The oscillation does not affect the fluid’s behavior during flow, ensuring stable and accurate control.
How Duty Cycle Impacts Valve Operation
- 0% Duty Cycle: No power is supplied; the spring holds the plunger in the fully closed position.
- 100% Duty Cycle: Maximum power is supplied; the plunger is fully retracted, and the valve is completely open.
- Intermediate Duty Cycles: The plunger position and valve opening are proportional to the duty cycle, enabling precise modulation.
In a normally closed proportional solenoid valve, the default (de-energized) state is closed. Powering the solenoid coil generates a magnetic field that counteracts the return spring, lifting the plunger and opening the valve. By varying the control signal, users can accurately adjust the flow and pressure to meet process requirements.
Advantages of Proportional Solenoid Valves
Why choose a proportional solenoid valve over a standard on/off valve? Here are some key benefits:
- Precise Flow Control: Achieve accurate modulation of liquids, gases, or steam for optimal process performance.
- Improved Process Efficiency: Reduce energy consumption and minimize process variability by matching supply to demand.
- Fast Response: Rapid adjustment to changing control signals ensures tight process control in dynamic environments.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of media, including air, water, oil, fuel, inert gases, and aggressive chemicals (with appropriate materials).
- Compact Design: Space-saving construction is ideal for OEM equipment, process automation, and laboratory instrumentation.
- Reduced Maintenance: Fewer moving parts and electronic actuation result in lower wear and longer service life.
How to Select the Right Proportional Solenoid Valve
Selecting the optimal proportional solenoid valve is a critical decision that impacts process control, energy efficiency, and system reliability. Compared to simple on/off valves, precise sizing and specification are essential in continuous flow or modulating control applications. The right valve ensures you achieve target flow rates and pressures while avoiding issues such as excessive pressure drop, inadequate flow, or unstable operation.
Key Selection Criteria:
- Flow Coefficient (Kv or Cv): The valve’s flow coefficient, typically expressed as Kv (in metric units, m³/h), quantifies how much flow the valve can pass at a given pressure drop. Accurately calculating the required Kv value is critical for proper sizing.
- Pressure Range: Ensure the valve’s rated pressure range matches your application’s operating and maximum pressures. Undersized orifice or insufficient coil force can limit performance.
- Media Compatibility: The valve’s body, seals, and internal materials must be compatible with the process media (e.g., water, air, oil, aggressive chemicals, gases).
- Electrical Specifications: Match the control signal type (DC voltage, PWM, analog current), coil voltage, and connector types to your automation system’s requirements.
- Response Time: Fast-acting valves are critical where rapid adjustment to process changes is required.
- Power Consumption: Consider energy efficiency, especially for battery-powered or energy-sensitive installations.
- Port Size and Connection Type: Ensure compatibility with your piping or tubing system (threaded, flanged, push-fit, etc.).
- Temperature Range: Confirm the valve can withstand the process and ambient temperature conditions.
- Certifications and Standards: For regulated industries, ensure compliance with standards such as CE, UL, RoHS, ATEX, or FDA as needed.
Why Is Valve Sizing So Important?
In continuous flow applications, correct valve sizing is crucial. If the valve is oversized, full flow is achieved at a small opening, limiting control resolution and making precise regulation difficult. If the valve is undersized, it may not achieve the required maximum flow. A best practice is to size the valve so that the pressure drop across it is about 30% of the total system pressure drop.
Kv Calculation Formula:
- QN = Normal Flow rate [m³/hour]
- Kv = Hydraulic factor
- T = Inlet gas temperature [K]
- p1 = Inlet Pressure [bar]
- p2 = Outlet Pressure [bar]
- dp = Pressure differential [bar]
- SG = Specific Gravity (Air = 1)
After calculating the required Kv value and factoring in the application’s pressure range, select a valve with a Kv rating about 10% higher than the application’s peak requirement to ensure reliable operation and accommodate minor system variations.
Other Important Factors: Maximum operating pressure, compatibility with process media, response time, coil voltage, power consumption, and port connection type should all be carefully evaluated. Looking for corrosion-resistant materials or high-temperature designs? Many manufacturers offer custom solutions for demanding environments.
Search Prompt: What are the best proportional solenoid valves for high-pressure steam applications? Explore our [proportional solenoid valve selection guide](#) for recommendations by industry and media type.
Proportional Solenoid Valve Applications: Where Are They Used?
Proportional solenoid valves are found in a diverse range of industries and applications that demand precise, automated control of fluid or gas flow. Typical use cases include:
- Burner and Flame Control: Industrial burners require accurate fuel-to-oxidizer ratios for efficient combustion. Proportional valves modulate gas and air flows to maintain optimal flame characteristics, improving energy efficiency and reducing emissions.

- Level Control and Pressurization: Used in tank level management, proportional valves—often paired with PID controllers—maintain consistent fluid pressure by adjusting air or nitrogen supply, ensuring stable process conditions and preventing over-pressurization.
- Mixing and Blending: In food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and chemical processing, proportional solenoid valves enable accurate mixing of cold and warm water or other fluids, maintaining target temperatures and concentrations with feedback from temperature sensors.
- Temperature Control: In HVAC and process cooling/heating systems, proportional valves regulate the flow of chilled or heated water through heat exchangers or coils, delivering precise temperature control for critical processes. For example, a solenoid control valve can modulate water supply based on real-time temperature feedback.
- Direct Flow Control: In laboratory automation, medical devices, analytical instruments, and industrial machinery, proportional valves enable direct and responsive control of gas or liquid flows, supporting dosing, sampling, and dispensing applications.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Used in fuel injection, emission controls, and hydraulic or pneumatic actuation systems for real-time adjustment and optimal performance.
- Water Treatment and Environmental: Proportional valves manage dosing of chemicals, pH control, and flow balancing in municipal water, wastewater, and environmental monitoring systems.
- Medical and Analytical Equipment: Enable precise fluid metering for anesthesia, dialysis, gas mixing, and chromatography systems.
- Industrial Automation: Integrated into control panels and PLC systems for process automation, machine tool cooling, and robotic applications.
Search Prompt: How do proportional solenoid valves improve energy efficiency in HVAC systems? Check out our [HVAC application insights](#) for case studies and energy-saving tips.
Comparison: Proportional vs. On/Off Solenoid Valves
If you’re deciding between proportional and standard on/off solenoid valves, consider the following:
- Control: Proportional valves offer continuous modulation, while on/off valves provide only binary (open/closed) control.
- Precision: Proportional valves excel in applications requiring fine control; on/off valves suit simple, non-modulating tasks.
- Complexity: Proportional valves require more sophisticated control signals and system integration.
- Cost: Proportional valves are typically more expensive but deliver greater value in critical process applications.
Action Prompt: Need help deciding which valve type fits your process? Contact our [technical support team](#) or browse our [valve selection FAQ](#).
Proportional Solenoid Valve Technologies and Variants
Proportional solenoid valves can be categorized by actuation method, valve body construction, and application-specific features:
- Direct-Acting Proportional Valves: The solenoid directly moves the plunger or spool, ideal for low-flow and fast-response applications.
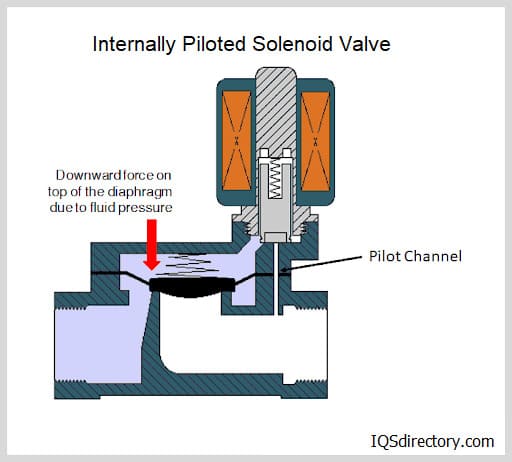
- Pilot-Operated Proportional Valves: Use pilot pressure to assist in opening larger valves, enabling higher flow rates with lower coil power.
- 2-Way, 3-Way, and 4-Way Configurations: Choose the right flow path and port arrangement for your system’s needs.
- Explosion-Proof and High-Temperature Designs: For hazardous environments, select valves with ATEX, IECEx, or FM approval.
- Analog, Digital, or Fieldbus Interfaces: Modern valves support integration with PLCs, DCS, or IoT-enabled systems.
Search Prompt: Which proportional solenoid valve technology is best for dosing aggressive chemicals? See our [chemical compatibility guide](#).
How to Choose the Best Proportional Solenoid Valve Supplier
Selecting a reliable proportional solenoid valve supplier is essential for ensuring product quality, technical support, and on-time delivery. Here’s how to make an informed decision:
- Compare Multiple Suppliers: Use our [proportional solenoid valve directory](#) to review at least four reputable vendors. Evaluate each supplier’s product range, technical expertise, and industry certifications.
- Review Business Profiles: Each supplier’s profile highlights areas of specialization, manufacturing capabilities, and customer service quality.
- Request Quotes and Technical Data: Use our integrated contact forms to ask for pricing, lead times, CAD drawings, datasheets, and application engineering support.
- Website Preview: Visit supplier websites using our proprietary previewer for a quick overview of expertise and core offerings.
- Send RFQs: Streamline your procurement process by submitting a single RFQ to multiple suppliers simultaneously.
- Check References and Reviews: Look for testimonials, case studies, and third-party reviews to assess supplier reliability and after-sales service.
Action Prompt: Ready to request a quote or technical consultation? Use our [RFQ form](#) to contact leading proportional solenoid valve manufacturers today.
Frequently Asked Questions About Proportional Solenoid Valves
- What is the difference between a proportional valve and a servo valve?
Servo valves offer higher precision and faster response, often used in closed-loop hydraulic or pneumatic systems, while proportional solenoid valves provide cost-effective and reliable control for most industrial automation applications. - How do I troubleshoot a proportional solenoid valve that isn’t responding?
Check for proper control signal, verify coil voltage, inspect for debris or contamination, and ensure the valve is not stuck due to corrosion or wear. Refer to your supplier’s troubleshooting guide or contact technical support. - Can proportional solenoid valves be used for both liquids and gases?
Yes, as long as the valve materials and design are compatible with the media and operating conditions. - Are proportional solenoid valves suitable for food and pharmaceutical applications?
Many manufacturers offer hygienic and FDA-compliant designs with food-grade materials for clean-in-place (CIP) and sanitary processing. - What maintenance is required for proportional solenoid valves?
Regular inspection for leaks, cleaning of orifices, and checking electrical connections are recommended to ensure long-term performance.
Search Prompt: Still have questions about proportional solenoid valves? Explore our [comprehensive FAQ page](#) or ask an expert.
Conclusion: Why Invest in Proportional Solenoid Valves?
Proportional solenoid valves are a critical enabler for modern process automation, fluid handling, and precision control applications. Whether you are optimizing a manufacturing line, automating laboratory workflows, or improving energy efficiency in HVAC and water treatment systems, the right proportional solenoid valve delivers superior control, reliability, and long-term value.
When choosing a proportional solenoid valve, focus on application requirements, media compatibility, and supplier reliability. Leverage our expert resources, selection guides, and supplier directory to make an informed decision and maximize your project’s success.
Ready to upgrade your flow control? Browse leading proportional solenoid valve brands or connect with our technical advisors to discuss your needs.










 Ball Valves
Ball Valves Butterfly Valves
Butterfly Valves Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps Check Valves
Check Valves Diaphragm Valves
Diaphragm Valves Flow Meters
Flow Meters Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pumps Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic Valves Metering Pumps
Metering Pumps Solenoid Valves
Solenoid Valves Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum Pumps Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services